As an Amazon FBA seller, understanding how to accurately calculate your profit margins and costs is crucial to your business’s success. Whether you’re just starting with Amazon product research or already managing your FBA business, knowing your Amazon FBA costs, operating expenses, and profit potential helps you make better decisions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will show you step-by-step how to calculate your Amazon FBA profit margin, ensuring that you price your products for maximum profitability.
Let’s dive in!
Types of Amazon Profit Margins
Before diving into how to calculate your margins, it’s essential to understand the types of profit margins you’ll encounter as an Amazon FBA seller:
- Gross Profit Margin: This refers to your total product sales revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS). It’s a measure of product profitability before operating expenses are deducted.
- Operating Profit Margin (Net Margin): This takes into account all costs associated with running your business, including Amazon fees, operating expenses, and shipping costs. The net margin represents your actual business profitability after all deductions.
Key Amazon FBA Fees to Consider
When selling on Amazon FBA, there are several fees you must account for in your profit margin calculations:
- Referral Fee: A percentage of your product’s selling price paid to Amazon for each sale.
- Seller Account Fee: The monthly fee paid to maintain your seller account (individual or professional plans).
- FBA Fees: Fees associated with using Amazon’s fulfillment services, including storage and per-unit shipping fees.
- Variable Closing Fee: Charged based on the shipping category and costs of the item.
Being aware of these fees will help you calculate your Amazon FBA profit margin more accurately.
How to Calculate Amazon FBA Profit Margin
Now that you know the types of margins and fees involved, here’s how to calculate your Amazon FBA profit margin. Let’s break it down into a few key steps:
Gross Profit Margin Formula:
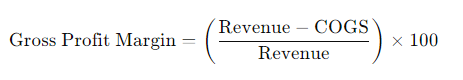
Revenue: Total sales price of your product.
COGS: Cost of goods sold, including production and shipping costs to Amazon.
Operating Profit Margin Formula:
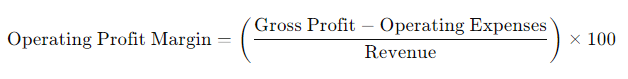
By using these formulas, you can calculate your gross and net profit margins to evaluate product profitability on Amazon.
Important Considerations for Profit Margin Calculation
- Think Long-Term: Short-term strategies, like temporarily lowering your margins to increase sales, may help you scale your business in the beginning, but long-term profitability requires consistent focus on margins.
- Understand Your Business: Profit margins differ across industries and product categories. What’s profitable for one Amazon seller may not be the same for another. Ensure you do thorough research before setting prices.
- Always Account for Amazon Fees: Include all Amazon fees (referral, FBA, storage, and shipping) in your calculations to avoid underpricing your products.
The 3X Rule for Amazon Sellers
A popular pricing strategy for new Amazon FBA sellers is the 3X Rule. This rule suggests that you price your products at three times their cost, broken down as follows:
- Cost: The cost of goods sold (COGS), including manufacturing and shipping.
- Fee: Amazon fees, including FBA and referral fees.
- Profit: A 100% return on investment (ROI).
While this rule can be a great starting point, it may not always be the most accurate. For better results, use the profit margin formulas outlined earlier to calculate specific margins.
How to Increase Your Amazon FBA Profit Margin
To maximize your profit margin, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Use Repricing Software: Automate price changes based on market fluctuations with repricing software. This helps keep your products competitively priced without constant manual adjustments.
- Bundle Products: Offering product bundles can attract buyers and increase sales volume, which in turn boosts your profit margins.
- Use Credit Cards for Inventory Purchases: Pay for inventory with a credit card to earn points, cashback, and other rewards. Just ensure you pay off your balance to avoid interest charges.
- Buy Out Suppliers: If your supplier has limited stock, consider purchasing all remaining units. This reduces competition and increases your chances of dominating the market for a specific product.
- Monitor Supplier Prices: Keep an eye on your suppliers’ prices. When costs drop, bulk-buy products and resell them at a higher price for greater profit margins.
- Capitalize on Out-of-Stock Products: If a product goes out of stock but has high demand, take advantage by quickly restocking and capturing sales before competitors return.
How to Accurately Calculate Amazon FBA Profit Margin and Costs | Eforce Ventures
As an Amazon FBA seller, understanding how to accurately calculate your profit margins and costs is crucial to your business’s success. Whether you’re just starting with Amazon product research or already managing your FBA business, knowing your Amazon FBA costs, operating expenses, and profit potential helps you make better decisions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will show you step-by-step how to calculate your Amazon FBA profit margin, ensuring that you price your products for maximum profitability.
Let’s dive in!
Types of Amazon Profit Margins
Before diving into how to calculate your margins, it’s essential to understand the types of profit margins you’ll encounter as an Amazon FBA seller:
- Gross Profit Margin: This refers to your total product sales revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS). It’s a measure of product profitability before operating expenses are deducted.
- Operating Profit Margin (Net Margin): This takes into account all costs associated with running your business, including Amazon fees, operating expenses, and shipping costs. The net margin represents your actual business profitability after all deductions.
Key Amazon FBA Fees to Consider
When selling on Amazon FBA, there are several fees you must account for in your profit margin calculations:
- Referral Fee: A percentage of your product’s selling price paid to Amazon for each sale.
- Seller Account Fee: The monthly fee paid to maintain your seller account (individual or professional plans).
- FBA Fees: Fees associated with using Amazon’s fulfillment services, including storage and per-unit shipping fees.
- Variable Closing Fee: Charged based on the shipping category and costs of the item.
Being aware of these fees will help you calculate your Amazon FBA profit margin more accurately.
How to Calculate Amazon FBA Profit Margin
Now that you know the types of margins and fees involved, here’s how to calculate your Amazon FBA profit margin. Let’s break it down into a few key steps:
- Gross Profit Margin Formula:Gross Profit Margin=(Revenue−COGSRevenue)×100\text{Gross Profit Margin} = \left( \frac{\text{Revenue} – \text{COGS}}{\text{Revenue}} \right) \times 100Gross Profit Margin=(RevenueRevenue−COGS)×100
- Revenue: Total sales price of your product.
- COGS: Cost of goods sold, including production and shipping costs to Amazon.
- Operating Profit Margin Formula:Operating Profit Margin=(Gross Profit−Operating ExpensesRevenue)×100\text{Operating Profit Margin} = \left( \frac{\text{Gross Profit} – \text{Operating Expenses}}{\text{Revenue}} \right) \times 100Operating Profit Margin=(RevenueGross Profit−Operating Expenses)×100
- Operating Expenses: This includes Amazon FBA fees, referral fees, seller account fees, and any additional business costs.
By using these formulas, you can calculate your gross and net profit margins to evaluate product profitability on Amazon.
Important Considerations for Profit Margin Calculation
- Think Long-Term: Short-term strategies, like temporarily lowering your margins to increase sales, may help you scale your business in the beginning, but long-term profitability requires consistent focus on margins.
- Understand Your Business: Profit margins differ across industries and product categories. What’s profitable for one Amazon seller may not be the same for another. Ensure you do thorough research before setting prices.
- Always Account for Amazon Fees: Include all Amazon fees (referral, FBA, storage, and shipping) in your calculations to avoid underpricing your products.
The 3X Rule for Amazon Sellers
A popular pricing strategy for new Amazon FBA sellers is the 3X Rule. This rule suggests that you price your products at three times their cost, broken down as follows:
- Cost: The cost of goods sold (COGS), including manufacturing and shipping.
- Fee: Amazon fees, including FBA and referral fees.
- Profit: A 100% return on investment (ROI).
While this rule can be a great starting point, it may not always be the most accurate. For better results, use the profit margin formulas outlined earlier to calculate specific margins.
How to Increase Your Amazon FBA Profit Margin
To maximize your profit margin, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Use Repricing Software: Automate price changes based on market fluctuations with repricing software. This helps keep your products competitively priced without constant manual adjustments.
- Bundle Products: Offering product bundles can attract buyers and increase sales volume, which in turn boosts your profit margins.
- Use Credit Cards for Inventory Purchases: Pay for inventory with a credit card to earn points, cashback, and other rewards. Just ensure you pay off your balance to avoid interest charges.
- Buy Out Suppliers: If your supplier has limited stock, consider purchasing all remaining units. This reduces competition and increases your chances of dominating the market for a specific product.
- Monitor Supplier Prices: Keep an eye on your suppliers’ prices. When costs drop, bulk-buy products and resell them at a higher price for greater profit margins.
- Capitalize on Out-of-Stock Products: If a product goes out of stock but has high demand, take advantage by quickly restocking and capturing sales before competitors return.
Amazon FBA Costs to Consider in 2024
Knowing all potential costs will give you a clear idea of your overall expenses and profit margins:
- Direct Costs: These are the costs of producing or purchasing products, including manufacturing, shipping, and packaging.
- Indirect Costs: This includes costs like insurance, warehouse fees, utilities, business travel, and software expenses.
- Amazon Fees: FBA fulfillment fees, storage fees, referral fees, and shipping costs. Be sure to account for these fees in your profit calculations.
- Handling Returns: Returns can incur additional costs if items can’t be resold at the original price.
Use the Amazon FBA Calculator
Amazon’s FBA calculator is an invaluable tool for accurately determining your costs and profit margins. Here’s how to use it:
- Navigate to the product’s page on Amazon.
- Enter product cost, shipping costs, and total unit cost into the FBA calculator.
- Hit “Calculate” to get a detailed breakdown of fees and potential profits.
This tool helps you make informed pricing decisions and ensures that your product remains profitable on Amazon.
Conclusion: Master Your Amazon FBA Profit Margin Calculation
Accurately calculating your Amazon FBA profit margin and costs is key to making smart business decisions and staying profitable. By using the formulas, strategies, and tools outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your Amazon FBA business is set up for long-term success.
At Eforce Ventures, we’re here to help you navigate the complexities of Amazon FBA, from product research to pricing strategies. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you succeed on Amazon!






